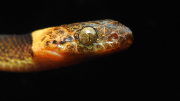
Northern Cat-Eyed Snake (Leptodeira septentrionalis)
Description: The northern cat eye is medium size (up to 3.3feet). In general females are slightly longer than males. They have smooth scales, with dark brown line or spot beside the eye and dark brown blotches (which can fuse to form a zigzag) running down their backs, these spots may vary in pattern geographically. Its head is distinctly wider than its neck and it has large bulging eyes with reddish irises and light brown elliptical pupils.
Habitat: Leptodeira septentrionalis can be found in a multitude of environments ranging from semi-arid scrub to rain forests. Within it's Texan range, Leptodeira septentrionalis prefers semi-arid, thorn brush habitats with ponds or streams in which to hunt breeding amphibians and their eggs.
Range: The northern cat eye is found in North America: US (S Texas), Mexico (Chiapas, Nuevo León, Quéretaro, Oaxaca, Puebla, Coahuila, Jalisco, Campeche, Yucatán, Quintana Roo, Nayarit), Guatemala, Honduras, Belize, El Salvador, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica. It is found at elevations of 0–6,365 feet above sea level.
Found in these States:
TX
Diet: it hunts for frogs and their eggs, it is particularly known for feeding on those of the red-eyed tree frog. It swallows eggs and small frogs alive but kills larger frogs with mild venom from its enlarged, grooved rear fangs.
Reproduction: The Northern cat eye is oviparous and produces clutches of 6–13 eggs. As in other snake species delayed egg fertilisation can occur (fertile eggs can be laid up to several years after copulation). Developing snakes are nourished by a yolk sac for 79 to 90 days at which time they break through the outer shell using an egg tooth. The egg tooth is lost after hatching. Young northern cat-eyed snakes appear identical to adults but feature much fresher coloration. The snakes will continue to grow throughout their entire lives.
Status: Listed as Least Concern because it is relatively widespread, and because it is not declining fast enough for listing in a more threatened category.
»» Kingdom: Animalia - Animals
»» Phylum: Chordata - Chordates
»» Subphylum: Vertebrata - Vertebrates
»» Class: Reptilia - Reptiles
»» Order: Squamata - Scaled Reptiles
»» Suborder: Serpentes
»» Superfamily: Colubroidea
»» Family: Colubridae - Colubrids
»» Genus: Leptodeira
»» Species: Leptodeira septentrionalis - Northern Cat-Eyed Snake
This article uses material from the Wikipedia article "Leptodeira septentrionalis", which is released under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share-Alike License 3.0. Content may have been omitted from the original, but no content has been changed or extended.
|